Services
Microbiology
Microbiology is the study of microscopic organisms, such as bacteria, viruses, archaea, fungi and protozoa. This discipline includes fundamental research on the biochemistry, physiology, cell biology, ecology, evolution and clinical aspects of microorganisms, including the host response to these agents.

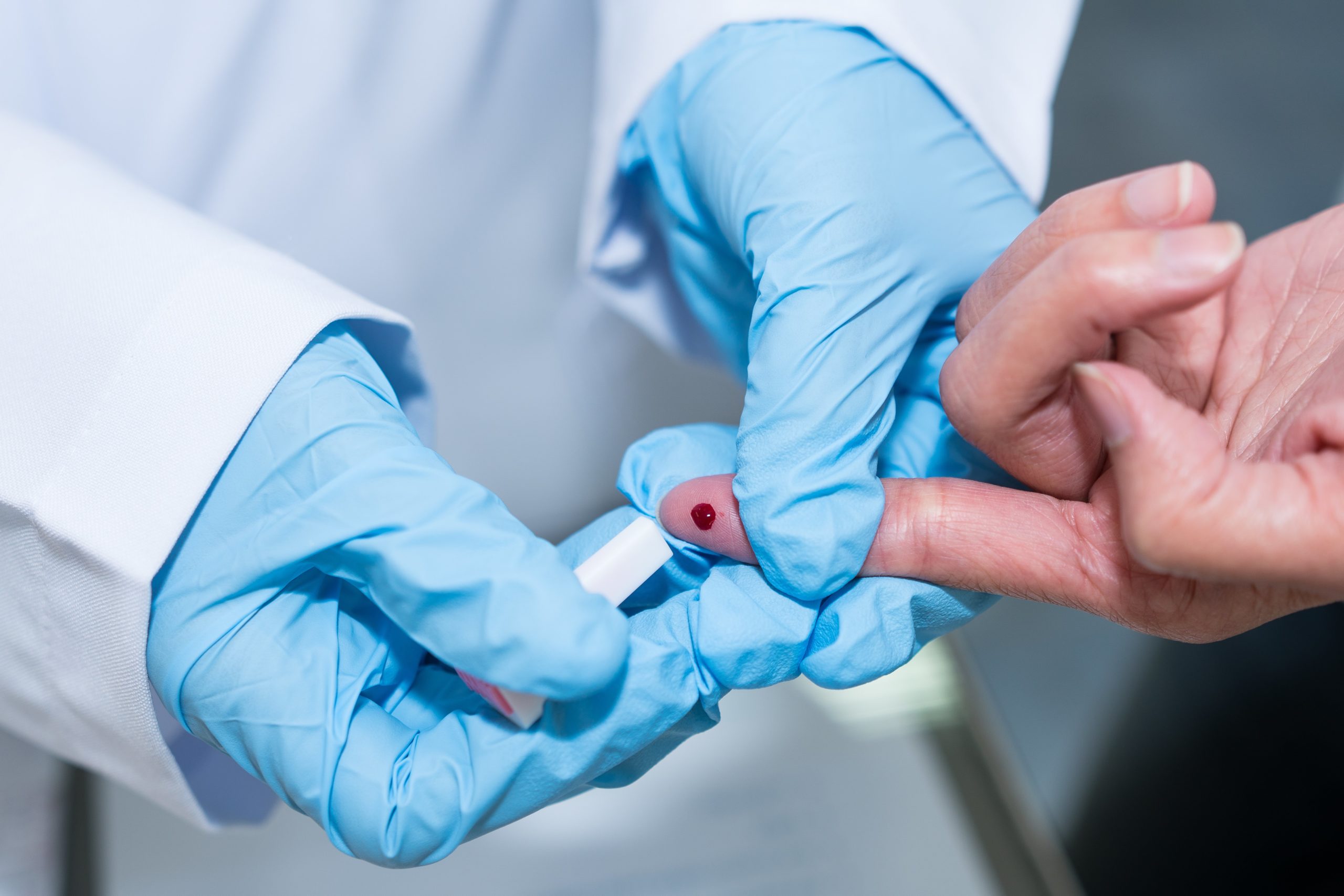
Serology
Serologic tests are blood tests that look for antibodies in your blood. They can involve a number of laboratory techniques. Different types of
serologic tests are used to diagnose various disease conditions.
Serologic tests have one thing in common. They all focus on proteins made by your immune system. This vital body system helps keep you healthy by destroying foreign invaders that can make you ill. The process for having the test is the same regardless of which technique the laboratory uses during serologic testing.

Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that concerns the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including molecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms and interactions.

Histopathology
Histopathology is the process of examining tissues to know more about the disease and the root cause behind it. The tissues are observed under a microscope in a histopathology laboratory. The process involves conducting a biopsy. Before starting the examination, the tissue is prepared, after which it gets treated and then analysed. Histopathology services are availed keeping in mind the type of tissue being examined as well as the type of investigation conducted.

Cytopathology
Cytopathology (from Greek κύτος, kytos, "a hollow"; πάθος, pathos, "fate, harm"; and -λογία, -logia) is a branch of pathology that studies and diagnoses diseases on the cellular level. The discipline was founded by George Nicolas Papanicolaou in 1928.

Clinical Pathology
Clinical pathology is a medical specialty that is concerned with the diagnosis of disease based on the laboratory analysis of bodily fluids, such as blood, urine, and tissue homogenates or extracts using the tools of chemistry, microbiology, hematology and molecular pathology.

Hematology
Hematology is the science or study of blood, blood-forming organs and blood diseases. In the medical field, hematology includes the treatment of blood disorders and malignancies, including types of hemophilia, leukemia, lymphoma and sickle-cell anemia.
Biochemistry
Biochemistry is the branch of science that explores the chemical processes within and related to living organisms. It is a laboratory based science that brings together biology and chemistry. By using chemical knowledge and techniques, biochemists can understand and solve biological problems.

Immunohistochemistry
Microbiology is the branch of biology which deals with microscopic organisms like viruses, bacteria, algae, fungi, slime molds, and protozoa.Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues.
